方法一:暴力枚举
最容易想到的方法是枚举数组中的每一个数x,寻找数组中是否存在 target - x。
当我们使用遍历整个数组的方式寻找 target - x 时,需要注意到每一个位于 x
C 代码解法
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* twoSum(int* nums, int numsSize, int target, int* returnSize){
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; ++i){
for(int j = i + 1; j < numsSize; ++j){
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target){
int* ret = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2);
ret[0] = i;
ret[1] = j;
*returnSize = 2;
return ret;
}
}
}
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}C++ 代码解法
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int n = nums.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return {i, j};
}
}
}
return {};
}
};Python3 代码解法
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
n = len(nums)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
if nums[i] + nums[j] == target:
return [i,j]
return []Java 代码解法
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
int n = nums.length;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
for(int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j){
if(nums[0] + nums[1] == target){
return new int[]{i,j};
}
}
}
return new int[0];
}
}复杂度分析 时间复杂度:O(N^2),其中 N 是数组中的元素数量。最坏情况下数组中任意两个数都要被匹配一次。 空间复杂度:O(1)。
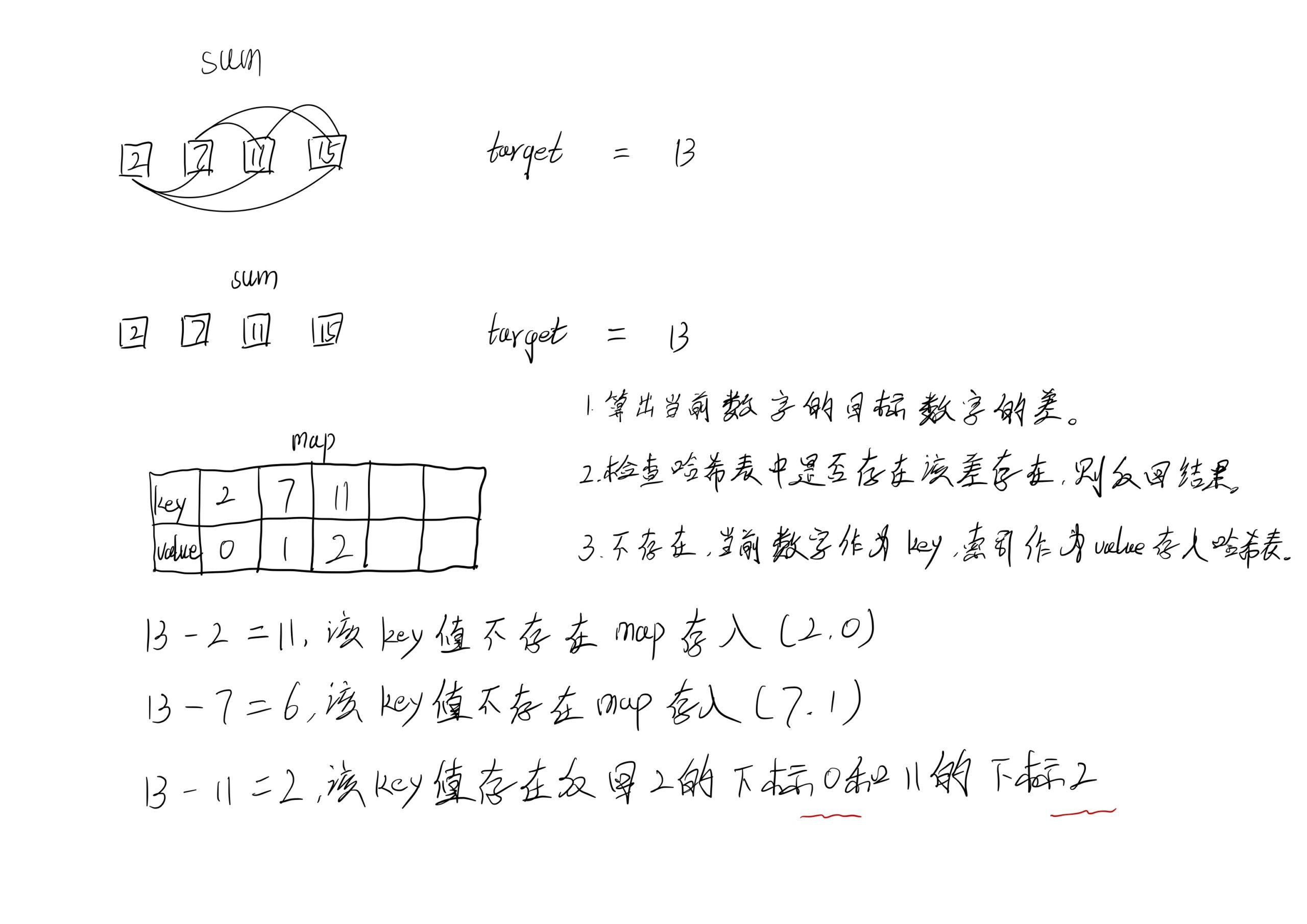
方法二:哈希表
注意到方法一的时间复杂度较高的原因是寻找到 target - x 的时间复杂度过高。因此,我们需要一个更优秀的方法,能够快速寻找数组中是否存在目标元素。如果存在,我们需要找出他的索引。
使用哈希表,可以将寻找 target - x 的时间复杂度降低到从 O(N) 降低到 O(1) 。
这样我们创建一个哈希表,对于每一个 x ,我们首先查询哈希表中是否存在 target - x,然后将 x 插入到哈希表中,即可保证不会让 x 和自己匹配。
Python 代码解法
class Solution:
def twoSum(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
hashtable = dict()
for i, num in enumerate(nums):
if target - num in hashtable:
return [hashtable[target - num], i]
hashtable[nums[i]] = i
return []Java 代码解法
class Solution {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> hashtable = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (hashtable.containsKey(target - nums[i])) {
return new int[]{hashtable.get(target - nums[i]), i};
}
hashtable.put(nums[i], i);
}
return new int[0];
}
}
Source: LeetCode(The title reproduced in this blog is for personal study use only)